
Stabilization of NaBH4 in Methanol Using a Catalytic Amount of NaOMe. Reduction of Esters and
COMMON REDUCING AGENTS LiAlH4 LITHIUM ALUMINIUM HYDRIDE (LAH) NaBH4 Non-selective reagent for hydride transfer reductions. Reacts with carboxylic acids, esters, lactones, anhydrides, amides and nitriles, converting them into alcohols and amines. Ketones, aldehydes, epoxides, alkyl halides are also reduced with lithium aluminium hydride.

Sodium Borohydride In Organic Chemistry
Sodium borohydride, also known as sodium tetrahydridoborate and sodium tetrahydroborate, [5] is an inorganic compound with the formula Na B H 4 (sometimes written as Na [BH4] ). It is a white crystalline solid, usually encountered as an aqueous basic solution.

LiAlH4 and NaBH4 Carbonyl Reduction Mechanism Chemistry Steps
NaBH4-FeCl2-mediated reduction showed high chemoselectivity, gave the desired products in magnificent yield (up to 96%), and was applied to synthesize a key intermediate of vilazodone (an.

Efficient and Simple NaBH4 Reduction of Esters at Cationic Micellar Surface Ester Chemical
Ester to Alcohol (NaBH 4) Examples: Example 1 To a suspension of the SM (500 mg, 0.99 mmol) in MeOH (50 mL) at 0 C was added NaBH4 (113 mg, 2.96 mmol). The reaction mixture was stirred at RT for 2 h. After concentration, the residue was diluted with H2O (100 mL) and extracted with EtOAc (3 x 30 mL).
PPT Alcohols PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4396111
Abstract. An intramolecular hydride delivery process largely contributes during the double reduction of α-keto esters into diols by NaBH 4. In the case of enolic α-keto esters, the first step of the process, the reduction of the keto group, occured exclusively through an 1,2-hydride addition despite the predominance of the tautomeric enolic form.

Aldehyde Ketone 17 I Reaction of Ester using LIAlH4 I NaBH4 I Reduction I Reactivity I Prof
This large-scale chirality at the interface of self-aggregates was exploited towards asymmetric resolution in ester reduction by NaBH 4. An enantiomeric excess of 53 % (( R )-2-phenylpropan-1-ol) was found in the case of the n -hexyl ester of 2-phenylpropionic acid as substrate in the aqueous aggregate of N , N ′-dihexadecyl- N , N , N ′, N ′-tetramethyl- N , N ′-ethanediyldiammonium.

LiAlH4 and NaBH4 Carbonyl Reduction Mechanism Chemistry Steps
This large-scale chirality at the interface of self-aggregates was exploited towards asymmetric resolution in ester reduction by NaBH4. An enantiomeric excess of 53% ((R)-2-phenylpropan-1-ol) was found in the case of the n-hexyl ester of 2-phenylpropionic acid as substrate in the aqueous aggregate of N,N'-dihexadecyl-N,N,N',N'-tetramethyl-N,N'-ethanediyldiammonium diquinate.

Scheme 1. Sodium borohydride (NaBH4) and diisobutylaluminum hydride... Download Scientific Diagram
In the sodium borohydride reduction the methanol solvent system achieves this hydrolysis automatically. In the lithium aluminium hydride reduction water is usually added in a second step. The lithium, sodium, boron and aluminium end up as soluble inorganic salts at the end of either reaction. Note!

Proposed mechanism for the reduction of nitroarenes using NaBH4... Download Scientific Diagram
Esters (including lactones) and amides are not reduced. As a source of hydride ion, NaBH will also act as a strong base, deprotonating water, alcohols, and carboxylic acids. also sees use in the reduction of organomercury bonds after oxymercuration reactions. 1. Sodium Borohydride (NaBH

PPT Chapter 21 The Chemistry of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives PowerPoint Presentation ID4011624
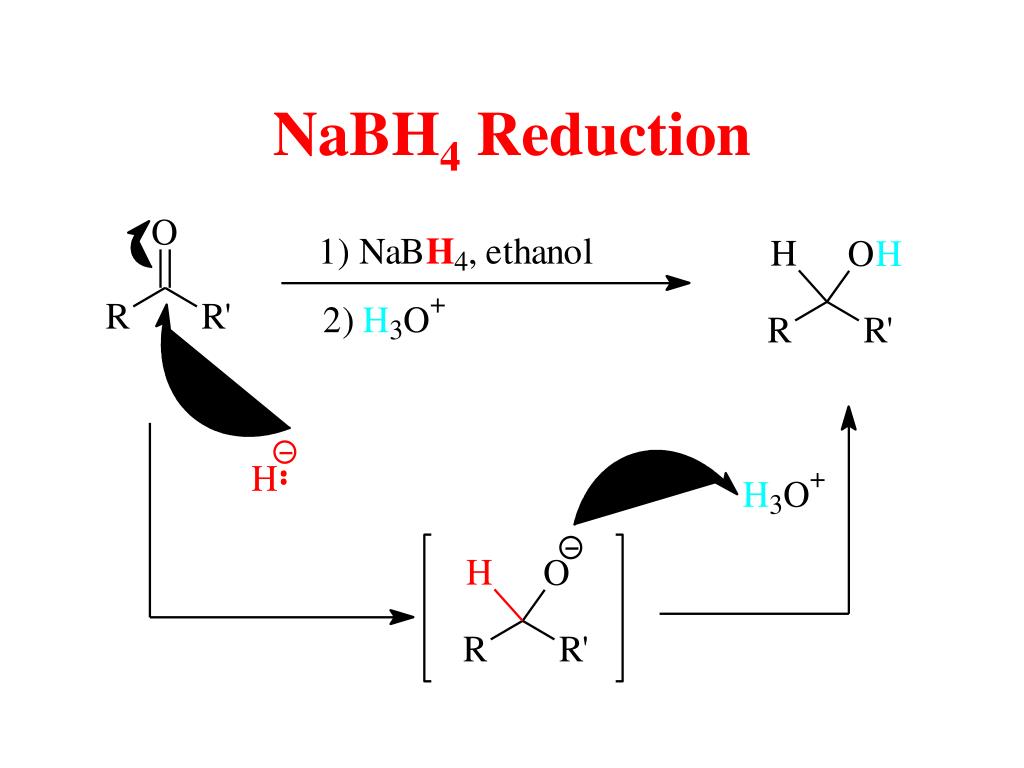
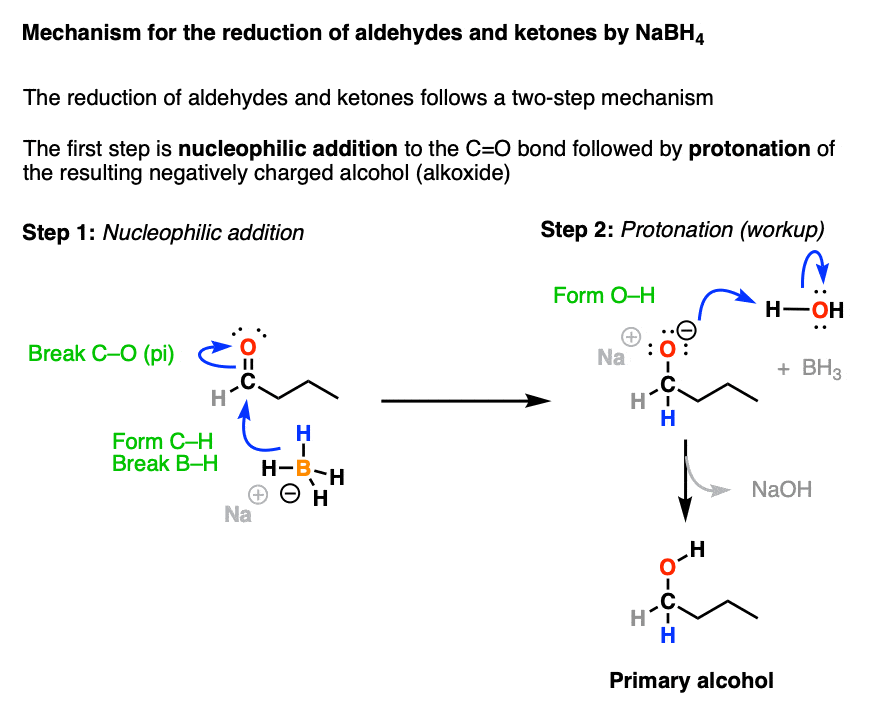
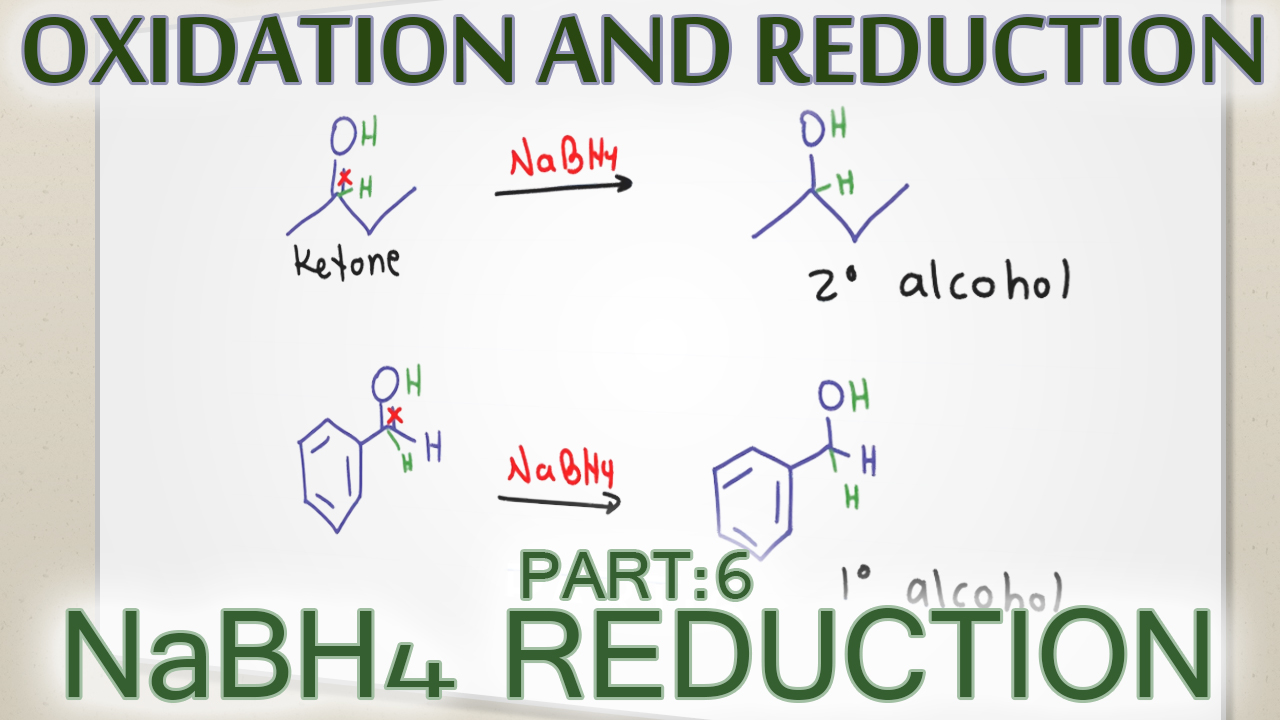
Organic Chemistry Reactions of Alcohols LiAlH4 and NaBH4 Carbonyl Reduction Mechanism Alcohols can be prepared from carbonyl compounds such as aldehydes, ketones, esters, acid chlorides and even carboxylic acids by hydride reductions. These reductions are a result of a net addition of two hydrogen atoms to the C=O bond:
Sodium Borohydride (NaBH4) As A Reagent In Organic Chemistry
In the sodium borohydride reduction the methanol solvent system achieves this hydrolysis automatically. In the lithium aluminium hydride reduction water is usually added in a second step. The lithium, sodium, boron and aluminium end up as soluble inorganic salts at the end of either reaction.. Reduction of carboxylic acids and esters.

LiAlH4 and NaBH4 Carbonyl Reduction Mechanism Chemistry Steps
Ester Reduction to a 1 o Alcohol. Esters can be converted to 1 o alcohols using LiAlH 4, while sodium borohydride (NaBH 4) is not a strong enough reducing agent to perform this reaction. The reduction of ethyl benzoate to benzyl alcohol and ethanol is shown as an example.
Sodium Borohydride Carbonyl Reduction Reaction and Mechanism
The electron rich and hindered ester, t-amyl-3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoate, also does not reduce under these conditions (with or without LiCl). However, both methyl and isopropyl 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoate esters were converted into 3,4,5-trimethyoxybenzyl alcohol in good yields in NaBH 4 /diglyme/LiCl at 162°C. These reductions did not occur unless.
Addition of NaBH4 to aldehydes to give primary alcohols Master Organic Chemistry
Rapid reaction of NaBH 4 with MeOH precludes its use as a solvent for large-scale ester reductions. We have now learned that a catalytic amount of NaOMe (5 mol %) stabilizes NaBH 4 solutions in methanol at 25 °C and permits the use of these solutions for the reduction of esters to alcohols. The generality of this reduction method was demonstrated using 22 esters including esters of naturally.
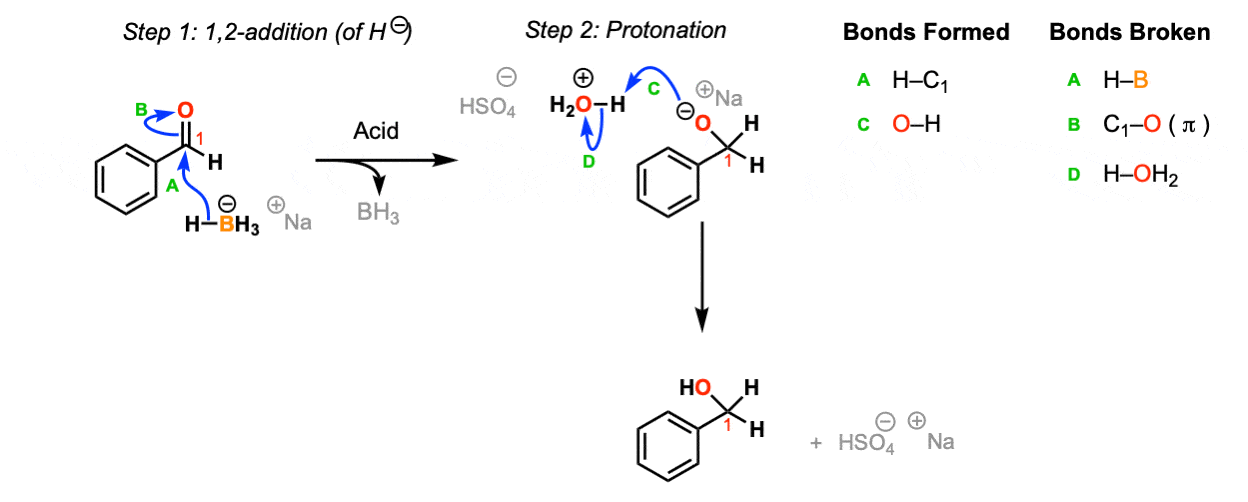
Addition of NaBH4 to aldehydes to give primary alcohols Master Organic Chemistry
Reduction of nitro, amide, carboxylate, ester and nitrile functional groups to -NH2, -CH2NH2, -CH2OH, -CH2OH and -CH2NCHPh, respectively were achieved using NaBH4 or NaBH4/LiCl in diglyme at 125.

Mechanism Study of βketo Ester Reduction using NaBH4/MeOH via Density Functional Theory
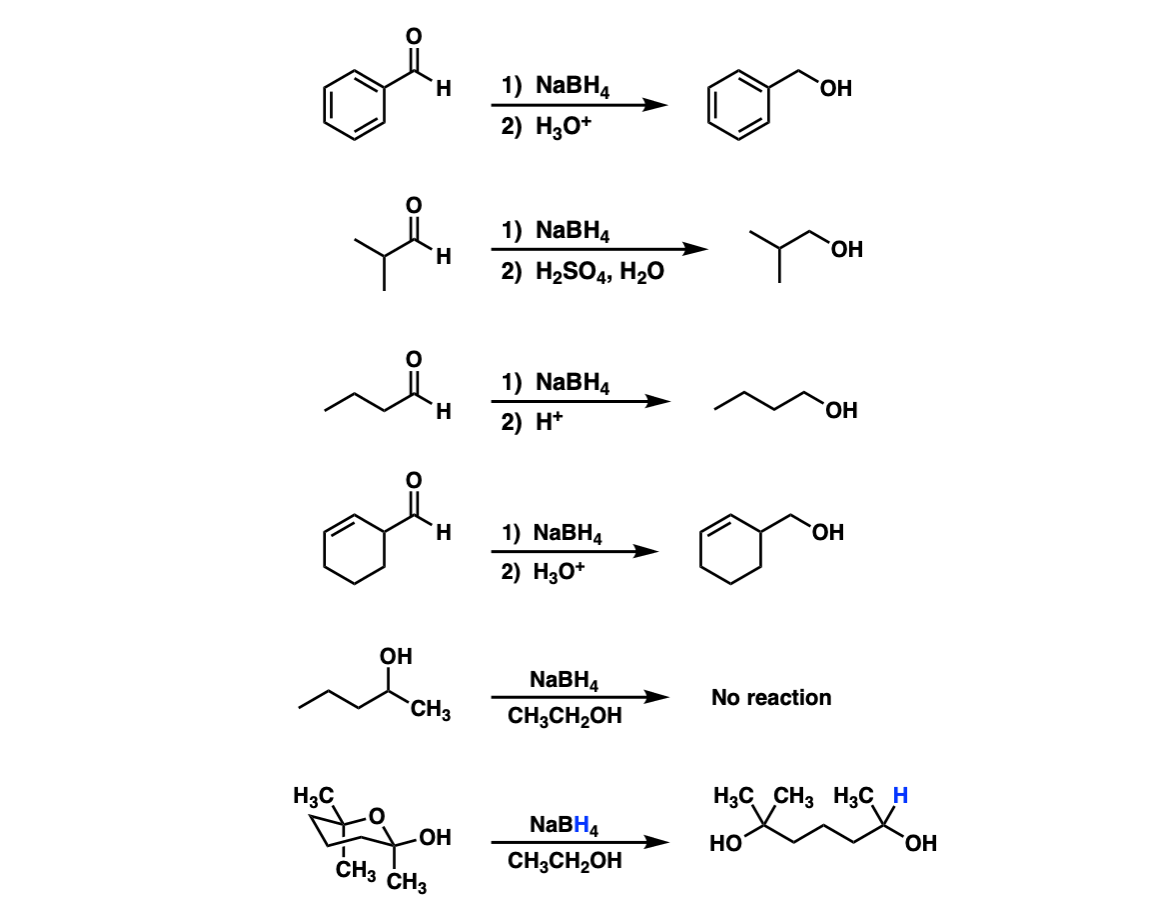
Sodium borohydride (NaBH 4) is not a reactive enough hydride agent to reduce esters or carboxylic acids. In fact, NaBH 4 can selectively reduce aldehydes and ketones in the presence of ester functional groups.. The mechanisms for the hydride reduction of esters is analogous to the hydride reduction of carboxylic acids. Nucleophilic acyl.